Table of Contents
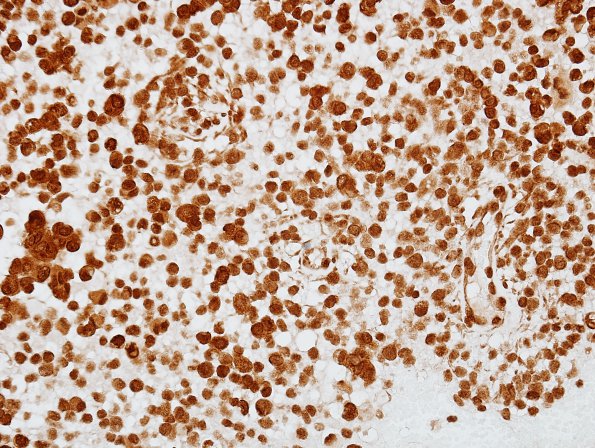
Washington University Experience | NEOPLASMS (MENINGIOMA) | Rhabdoid | 6D2 Meningioma, rhabdoid (2 yo, Case 6) BAF47 1.jpg
There is retention of nuclear staining in both tumor cells and in non-neoplastic endothelial cells for INI-1; this finding effectively rules out the diagnosis of atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor. ---- Ancillary studies (not shown): Vimentin staining is positive, and staining for S100, low molecular weight cytokeratin, GFAP and neuronal markers is negative. The Ki-67 proliferative index is described as low. Smooth muscle actin staining is limited to non-neoplastic blood vessels. ---- FISH was performed at Washington University to assess the status of chromosomal arms 22q, 14q and 1p, deletions of which are associated with meningiomas. In particular, 1p and 14q have been associated with atypical and anaplastic meningiomas as well as a higher risk of recurrence and shorter progression free survival. Also, the status of chromosomal arm 9p was investigated, since deletion of the p16 gene region on 9p has been associated with anaplastic meningiomas with shorter survival times. FISH probes showed normal dosages (i.e., two copies) of all chromosomes tested. These FISH results are therefore considered non-specific and do not exclude the light microscopic diagnosis of rhabdoid meningioma, particularly since genetic studies in patients this young are rare ---- Comment: The light microscopic features in this case are in keeping with a rhabdoid meningioma. By strict WHO criteria in place at the time of analysis (2007) this neoplasm would be graded as anaplastic (WHO 3). At that time it was commented that occasional cases of rhabdoid meningioma have been reported that otherwise lack clearcut "malignant" or anaplastic features, and due to limited clinical follow-up in these cases it is unclear whether such cases share the overall poor prognosis of the more classic examples with more obvious malignant features. Using criteria now in place we would probably consider this WHO Grade 2.