Table of Contents
Washington University Experience | PRION DISEASES | Prion Diseases | 17B2 CJD (Case 17) H&E 3
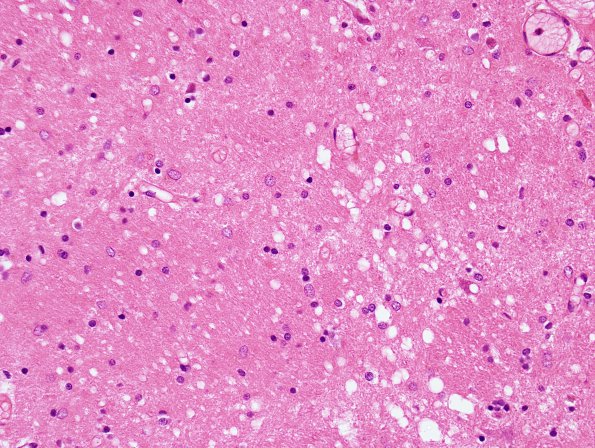
Sections of the frontal, temporal, and occipital cortex, as well as the basal ganglia and thalamus show spongiform change, neuronal loss, and prominent astrocytosis. The severity of vacuolation, neuronal loss, and gliosis is slightly increased in the thalamus and is greater in the frontal and temporal cortices relative to the occipital cortex. ---- Comment: At the NPDPSC immunostaining with 3F4 was positive. This finding established the diagnosis of prion disease, likely Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. In addition the prion protein gene (PrP) was characterized by Western blot and sequencing are consistent with the diagnosis of familial CJD associated with the E200K-129M mutation in the PrP gene.