Table of Contents
Washington University Experience | PRION DISEASES | Prion Diseases | 8E2 CJD (Case 8) L17 BG H&E 1
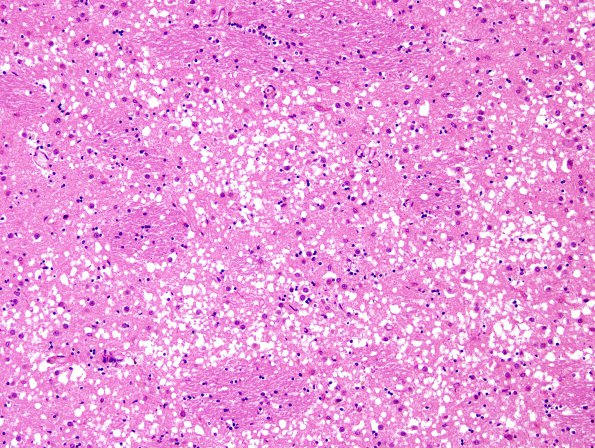
The basal ganglia are impressively involved. (H&E) ---- Comment: 3F4 immunohistochemistry failed to detect prion protein in the formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections. Independently, the NPDPSC detected only faint 'synaptic' prion positivity. The NPDPSC reported abnormal prion protein by immunoblot and absence of a familial PrP gene defect. ---- One unusual aspect of this case is the presence of large numbers of ballooned neurons in the cerebral cortex; similar cells have been described previously in CJD and corticobasal degeneration (Sakurai et al., PMID: 10965796; Budka, PMID: 14522854). The patient had no other neuropathologic features of corticobasal degeneration. ---- The case shows few foci of beta-amyloid plaques, sparse neuritic plaques, and only occasional neurofibrillary tangles. Using NIA-AA criteria, this case has AD neuropathologic change (A2B1C1) with a low likelihood the dementia is caused by Alzheimer’s disease. Lewy bodies were not present.